Contrast-enhanced mammogaphy (CEM)
What is contrast-enhanced mammography?
Contrast-enhanced mammography (CEM) is a breast imaging technique that combines a traditional mammogram with iodinated contrast dye (the same dye that is used for CT scans). The dye collects in abnormal blood vessels, making it possible to see breast cancers and other lesions that would otherwise not be visible on the mammogram.
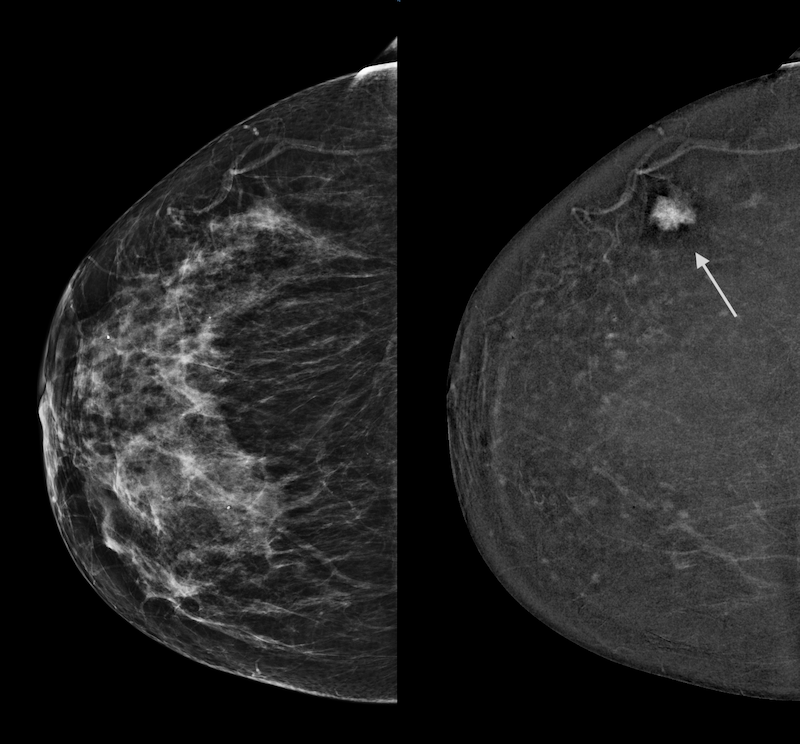
Here’s an example: 2 images of the same breast, on the same day. Traditional mammogram on left: the cancer is not visible. CEM image on the right is not limited by the dense tissue and highlights the cancer (arrow).
Who could benefit from a contrast-enhanced mammogram?
CEM is FDA-approved as a diagnostic tool for further evaluation of possible or known breast abnormalities. However, centers such as Memorial Sloan Kettering and a recent paper by Dr. Gilbert et al. in The Lancet have shown significant benefits in using CEM “off-label” for screening.
Screening CEM can be considered for all women with dense breasts, especially if they:
- have extremely dense breasts or
- have complex dense pattern (e.g., many cysts) or
- should be having breast MRI but can’t or aren’t (i.e., “high risk”) or
- are calculated to be at intermediate risk for breast cancer (using the Tyrer-Cuzick risk calculator) or
- are breast cancer survivors, especially if they were < 50 years old at the time of diagnosis
Diagnostic CEM can be considered for women who:
- have had a recent abnormal mammogram (i.e., callback) or
- are having short term follow up for a probably benign finding on a prior CEM or breast MRI study or
- have a recent diagnosis of breast cancer to assess for extent of disease in the affected breast and any hidden lesions in the opposite breast
What is involved in having a CEM study?
Prior to the CEM exam, the patient will be screened to make sure she can safely have a CEM exam. On the day of the study, an IV will be placed (arm or hand) and a dose of iodinated CT contrast is administered. After a short delay, the positioning and compression of the breast are the same as for a standard digital mammogram. The images are typically read while the patient is still at the imaging center, providing immediate results.
How does CEM compare to whole breast ultrasound, breast MRI, and tomosynthesis (3D mammogram)?
CEM has been shown to find 3-5 times more breast cancers than breast ultrasound. CEM detects nearly as many breast cancers as breast MRI but CEM has fewer false positives (false alarms) than breast MRI and most patients find CEM to be much more comfortable than breast MRI. CEM and tomosynthesis (3D) can be performed together at the same time; if an abnormality is identified, this “combo” exam can help with biopsy targeting. There is a nice table comparing the cancer detection of different imaging exams here.
What are the downsides of CEM?
CEM does add some radiation (the dose varies by patient and CEM device manufacturer), but the amounts are still within the accepted safety range for mammography. There is a risk of an adverse reaction to the contrast (same as with a CT scan). And “off-label” screening CEM is not yet covered by insurance.
Who should not have CEM?
Women who are pregnant, have uncontrolled kidney disease, or are allergic to iodine-based contrast should not have CEM.
What happens if CEM shows a highlighted area?
If a possible abnormality is identified, about 1/3 of the time a correlate can be found on ultrasound. If needed, CEM-guided biopsy can be performed.
Is a referral needed and what does it need to say?
Yes, a referral is needed for all CEM exams. For a screening CEM, the referral should say “screening mammogram with contrast and ultrasound if needed” or “screening CEM with ultrasound if needed.” For a diagnostic CEM, it can say “Diagnostic mammogram with contrast and ultrasound if needed” or “Diagnostic CEM with ultrasound if needed.” We ask for the order to include ultrasound so that ultrasound can be performed the same day if needed.
Is there anything that I should do prior to a CEM exam?
Drinking plenty of water prior to your exam can make IV access easier for you and the tech. As with a routine mammogram, do not wear deodorant, talcum powder, lotions, or oils on the day of your exam.
What happens after the exam?
Once the CEM imaging is complete, you will be monitored for a short period of time to ensure you tolerated the contrast well. During this time, your images will be reviewed. Sometimes, the CEM study may show areas that need additional imaging, such as ultrasound or more mammogram views. If that is the case, we will perform any necessary exams at this time and you will receive your results before you leave. We will send the final report to your ordering physician. Additionally, we recommend that you drink plenty of water for the rest of the day to help your kidneys filter out the contrast.
What is the cost of a contrast-enhanced mammogram?
Contrast-enhanced mammography is FDA approved as a diagnostic test but as such it would typically only be reimbursed as a 2D diagnostic mammogram which does not cover the costs of providing the exam. We are providing CEM “off-label” as an adjunctive screening test. “Off label” uses are common in medicine (examples include 3D/tomosynthesis screening when 1st introduced and Ozempic/similar weight loss drugs). As a screening test, CEM is not covered by insurance. We are currently charging $289 out of pocket, due at the time of the exam.


